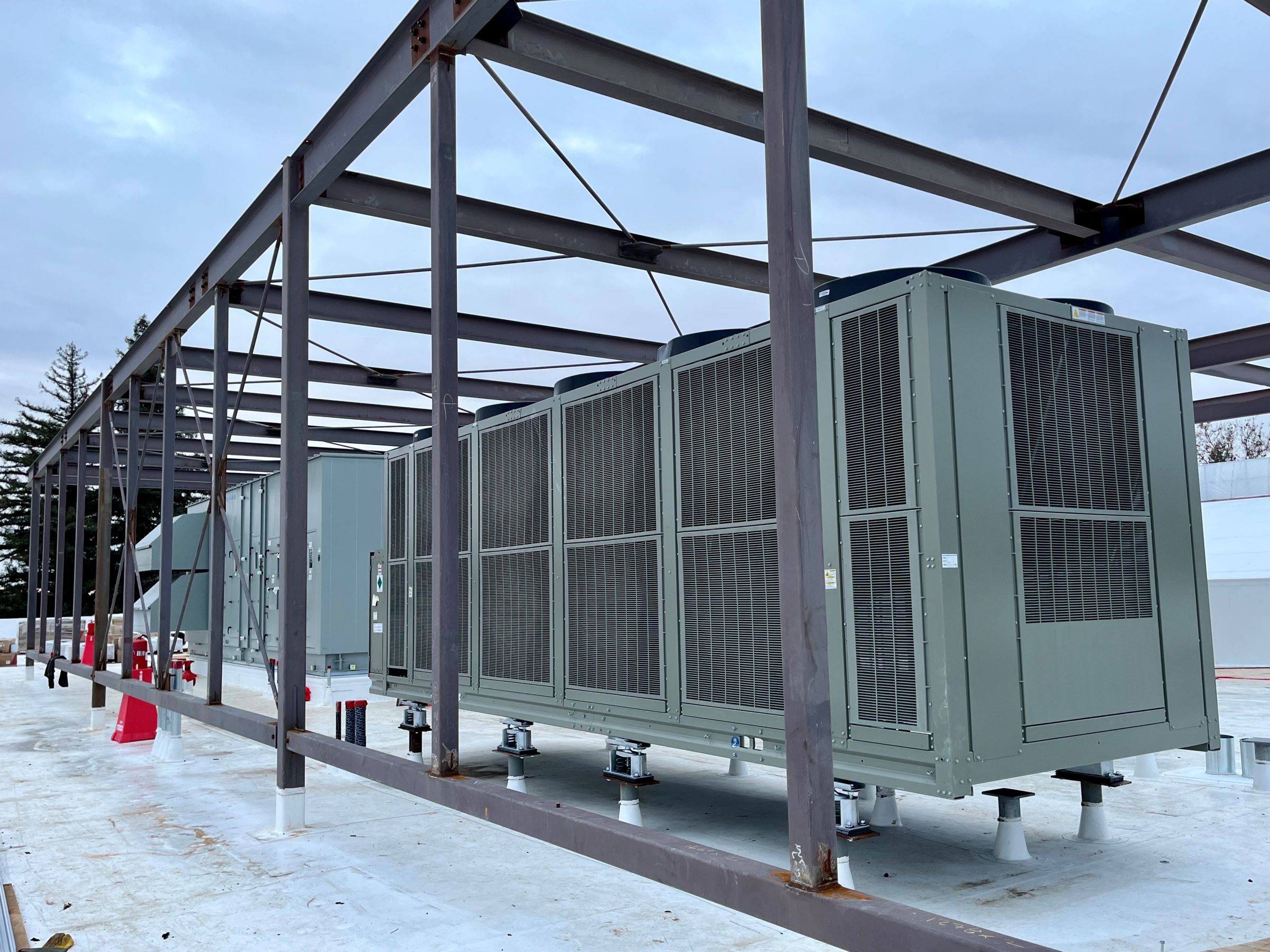

Heat pump systems offer a practical solution for achieving hot water decarbonization goals amid the pressing need to transition to sustainable energy sources. While conventional heat pumps face challenges in producing high hot water temperatures, advancements in commercial and industrial solutions such as the use of CO2 refrigerants, show promise. However, addressing temperature limitations and optimizing system configurations are crucial for effective implementation.
DECARBONIZATION IMPORTANCE
Heating and cooling contribute significantly to global energy consumption and carbon emissions. Heat pumps powered by low-carbon electricity are a practical solution to reduce heating costs and CO2 emissions, aiding in grid balance.
HEAT PUMP CHALLENGES
Most conventional heat pumps have limitations in producing high hot water temperatures (up to 140°F), which can be challenging for buildings designed for higher temperatures. Lower temperatures can affect efficiency and hot water recovery time, necessitating supplemental heating systems.
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL HEAT PUMP SOLUTIONS
Various types of air-to-water and water-to-water heat pumps are available for commercial and industrial applications. These systems can produce hot water temperatures ranging from 140°F to 180°F, with some utilizing CO2 refrigerants to reduce reliance on backup heating. Compound designs and advanced technologies enable operation at lower ambient conditions and higher efficiency.
Overall, heat pump systems offer a promising avenue for meeting hot water decarbonization goals, but considerations such as temperature limitations and system configurations must be addressed for effective implementation.
Click Here for Full Article
Get our latest business advice delivered directly to your inbox.