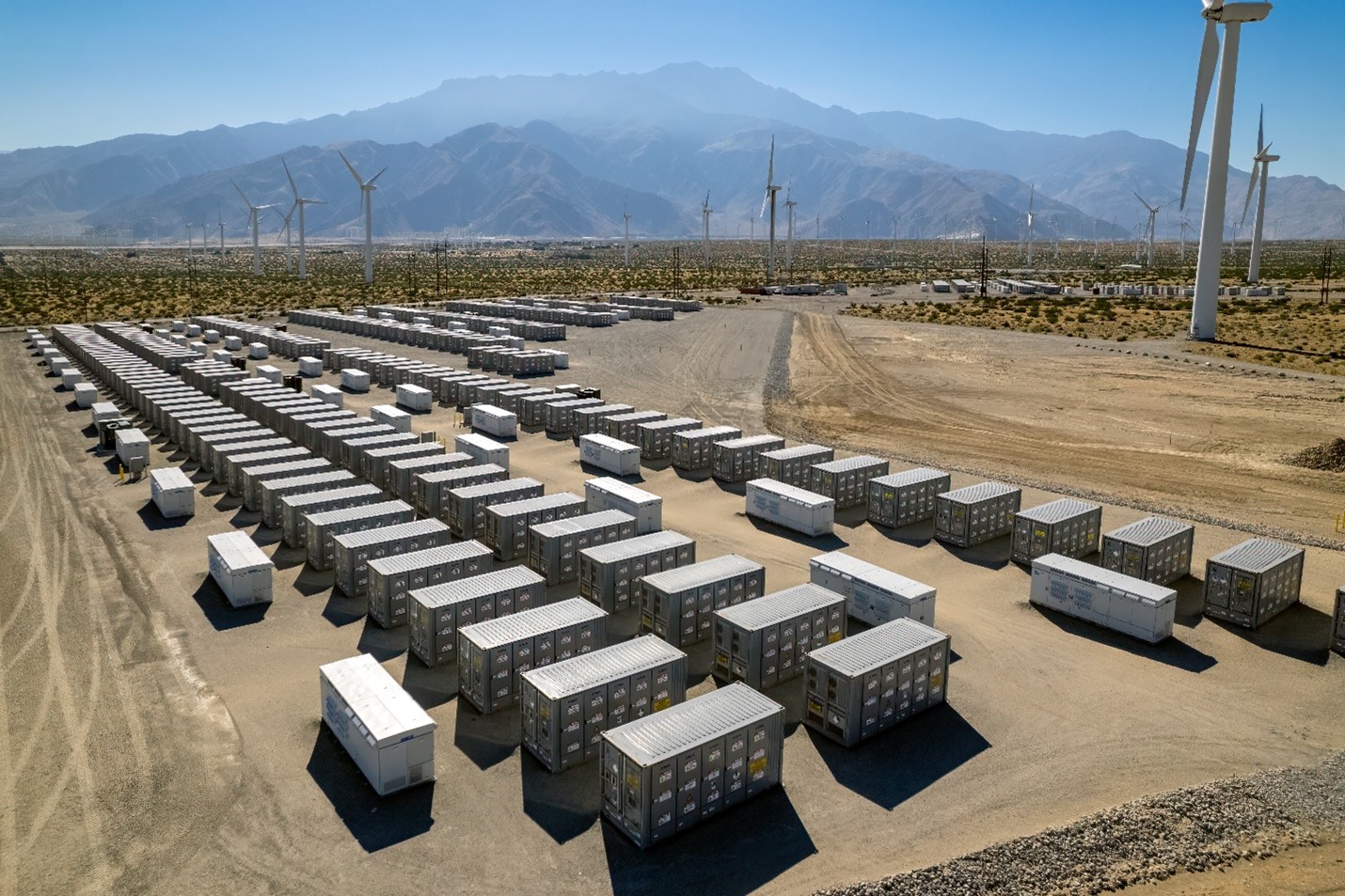

Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are a subset of the Energy Storage Systems (ESS) category. In the broader scope, ESS are comprised of any type of system that stores energy for future use through chemical, electrochemical, thermal, or mechanical means.
BESS systems use batteries (electrochemical) to store energy from various sources; the utility grid, and/or renewables, for conversion back to electrical energy when required. When connected to renewable energy sources such as wind or solar, BESS systems can provide stabilization and greater energy reliability by providing energy during times of energy uncertainty. When connected to the utility grid the BESS can provide peak demand relief and peak shaving. BESS systems can discharge and recharge quickly which allows the BESS to provide support to the grid or to the client side when required.
BESS can also provide backup power if the utility or renewable sources are no longer providing the power required by the connected system. The battery runtime can vary with typical storage durations from 2 to 10 hours depending on the system design and requirements. For direct utility connections where BESS is used for demand relief or peak shaving, the typical runtime is commonly designed to be 4 hours or less.
BESS installations are rated in Watts (kilo, Mega, or Giga) and Watt hours (kWh, MW,h or GWh). The Watt rating indicates the power capacity of the BESS and the Wh rating defines the amount of energy the system can supply. The Watthour rating is the system rating multiplied by the runtime of the battery system. For example, a 3 MW system that can supply 4 hours of runtime would be rated at 12 MWh.

Get our latest business advice delivered directly to your inbox.